![]()
Sun, June 19, 2011 | The Meir Amit Intelligence and Terrorism Information Center
The Muslim Brotherhood – Chapter 11: A profile of Sheikh Dr. Yusuf al-Qaradawi
The Muslim Brotherhood is an Islamic mass movement whose worldview is based on the belief that “Islam is the solution” and on the stated aim of establishing a world order (a caliphate) based on Islamic religious law (Shariah) on the ruins of Western liberalism. With extensive support networks in Arab countries and, to a lesser extent, in the West, the movement views the recent events in Egypt as a historic opportunity. It strives to take advantage of the democratic process for gradual, non-violent progress towards the establishment of political dominance and the eventual assumption of power in Egypt and other Middle Eastern countries.
Overview
Sheikh Dr. Yusuf Abdallah al-Qaradawi is a central figure affiliated with the Muslim Brotherhood. He was expelled from Egypt and found refuge in Qatar, and operates from there throughout the Muslim world.
After President Hosni Mubarak was ousted Al-Qaradawi returned to Egypt and delivered the Friday sermon at a mass rally held in Al-Tahrir Square in Cairo. Many consider him the supreme religious and ideological authority for the Muslim Brotherhood, although he is not officially its leader (in the past he refused to accept the title of the Muslim Brotherhood’s General Guide). He is influential in Egypt and considered one of the most important Sunni-Muslim clerics of our generation and a spiritual authority for millions of Muslims around the world, including the Hamas movement.
Al-Qaradawi’s popularity among the Sunnis has grown because of the massive use he makes of electronic media, including television and the Internet. One of his most important tools is the Qatari Al-Jazeera TV channel, which broadcasts his popular program “Life and Islamic Law” (Al-Sharia wal-Hayat), viewed by tens of millions of Muslims.
Al-Qaradawi has often exploited the program for blatant anti-Semitic propaganda and incitement (see below). He was also one of the founders of the IslamOnline website in 1997, which often quotes him.
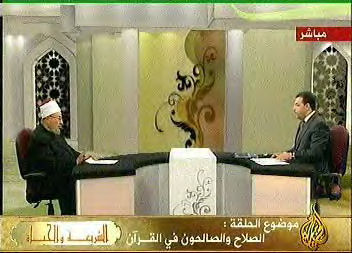
Sheikh Dr. Yusuf al-Qaradawi on Al-Jazeera TV's popular “Life and Islamic Law” program (Al-Jazeera TV, March 15, 2009).
Al-Qaradawi refers to his religious views as “moderate Islam,” which seeks to balance intellect and emotion. He has positive attitudes toward reforms in Islam, which he calls “correcting perceptions which were corrupted.” He is considered one of the foremost propounders of the doctrine of “the law of the Muslim minorities” (fiqh al-aqalliyyat) which provides the Muslim minorities around the globe with space in which to maneuver and compromise between their daily lives and Islamic law. The aim of implementing his doctrine is to unite and unify Muslim minorities to make it possible for them to live under non-Muslim regimes, until the final stage of spreading Islam to the entire world.
At the same time, building a bridge between the exigencies of Muslim emigrants’ daily lives and Islamic religious law also includes regarding taking over Europe as Islam’s next target. In 2003 Al-Qaradawi issued a fatwa declaring that “Islam will return to Europe as a victorious conqueror after having been expelled twice. This time it will not be conquest by the sword, but by preaching and spreading [Islamic] ideology […] The future belongs to Islam […] The spread of Islam until it conquers the entire world and includes both East and West marks the beginning of the return of the Islamic Caliphate […]”
Although Al-Qaradawi opposes Al-Qaeda and its methods, he enthusiastically supports Palestinian terrorism, including suicide bombing attacks targeting the civilian Israeli population. In the past he also expressed his support for the “resistance” (i.e., terrorism) to the occupation of Iraq, including, by implication – although he denied it — abducting and murdering American civilians in Iraq.
He issued fatwas calling for jihad against Israel and the Jews, and authorizing suicide bombing attacks even if the victims were women and children. He regards all of “Palestine” as Muslim territory (according to Muslim Brotherhood and Hamas ideology), strongly opposes the existence of the State of Israel and rejects the peace treaties signed with it, and opposes the Palestinian Authority (and in the past called for the stoning of Mahmoud Abbas).
Al-Qaradawi and the recent events in Egypt
In response to the dramatic events in Egypt, Al-Qaradawi (whose statements are widely reported in Egypt) expressed his support for the demonstrators. He called on the Egyptian people to fight the despots and forbade the security forces to shoot civilians. The IslamOnline website posted a chapter of his book [Islamic] Law and Jihad, according to which jihad against corruption and a tyrannical regime is the most exalted form of jihad, even more important than jihad against external enemies.
Al-Qaradawi was expelled from Egypt to Qatar in 1997 because of his affiliation with the Muslim Brotherhood, which was outlawed in Egypt. After Hosni Mubarak was ousted, Al-Qaradawi appeared at a rally attended by more than a million people in Cairo’s Al-Tahrir Square and delivered the Friday sermon (February 18, 2011). He expressed his esteem for the young people of Egypt who had revolted against the “despotic Pharaoh” Mubarak.
At the same time he sent a message of interfaith unity between Muslims and Christians, who had stood and demonstrated side by side. He praised the Egyptian army which had “adhered to freedom and democracy” and called for the immediate release of all political prisoners and for the rapid formation of a civilian government. He ended the sermon with a call for the liberation of Al-Aqsa mosque and asked the Egyptian army to open the Rafah crossing and allow aid convoys to enter the Gaza Strip (Al-Jazeera TV, February 18, 2011). A few days later, apparently on February 21, he returned to Qatar.
The Muslim Brotherhood, which until Al-Qaradawi’s arrival was careful to keep a low profile, was quick to declare that it was not behind the invitation that brought him to Egypt, apparently to prevent tensions with the other protest movements. Dr. Muhammad Sa’ad al-Katatni, Muslim Brotherhood spokesman, said that the Muslim Brotherhood had not invited Dr. Al-Qaradawi to Egypt, but rather that the invitation had come from the youth in Al-Tahrir Square (Al-Sharq al-Awsat, February 19, 2011). Spokesmen for other protest movements tried to diminish the importance of al-Qaradawi’s appearance.

Sheikh Al-Qaradawi speaks at a mass rally in Cairo’s Al-Tahrir square (Al-Jazeera TV, February 18, 2011).
Al-Qaradawi’s appearance at the rally in Cairo was a tribute to the great popularity he enjoys in Egypt and reflects a new stage in the Muslim Brotherhood’s public involvement in the events in Egypt. However, the statement made by the Muslim Brotherhood spokesman may indicate a potential rivalry and/or dissention between the Muslim Brotherhood leadership in Egypt and Al-Qaradawi, who entered the leadership vacuum which has plagued the Muslim Brotherhood in recent years.
Al-Qaradawi’s biography
Al-Qaradawi was born in a small Nile delta village in 1926. His father died when he was two and he grew up in his uncle’s house, in a religious environment. When he was four he was sent to a religious school. According to stories, when he was nine he knew the Quran by heart. As a youth he studied at a religious school in Tanta where he delved into the writings of Hassan al-Banna, the founder of the Muslim Brotherhood, who Al- Qaradawi said shaped his political and religious thinking.
When he was 18 he became a student in the religion department of Al-Azhar University in Cairo. He graduated in 1953. The following year he passed the exam to receive a teaching license. In 1958 he received a Master’s degree in Arab language and literature and in 1973 received a Doctorate. So far he has written more than 50 books about various aspects of Islamic jurisprudence. During his studies at Al-Azhar he was exposed to the Muslim Brotherhood ideology and devoted himself to political Islamic activity and to preaching against the British presence in Egypt. His preaching against Nasser’s regime led to his being arrested several times.
His Islamic political activity and sharp tongue caused him to be dismissed from Al-Azhar University in 1961 and assigned to head its branch in Qatar. However, sent to Qatar and released from the pressures of the Egyptian regime, enabled him to become prominent as an independent cleric. He has lived in Qatar since 1961, where he headed a high religious school. In 1977 he founded the Department of Islamic Law Studies in the University of Qatar and headed it until 1990. He also founded an institute for Sunna study.
To this day, the institutions he founded are important centers for his activity in the Arab-Muslim world and among Muslim communities in the West. He was granted Qatari citizenship in honor of the services he performed for the country. He has received a number of awards and decorations, among them the King Feisal of Saudi Arabia Award, the Islamic University of Malaysia Award and the Sultan of Brunei Award.
After the Muslim Brotherhood was outlawed in Egypt, al-Qaradawi became a wanted man and could not return to his home country. Until now he has lived in Qatar, where he has held a number of posts, both in and outside the country. They included head of the Qatar University’s institute for the study of the history of the prophet Muhammad; chairman of the association of Muslim scholars; head of the European Council for Fatwa and Research (ECFR — an Islamic-European umbrella organization for the rapprochement between Muslim communities throughout Europe and for building bridges between the various Islamic schools so that they can integrate life in democratic Christian Europe with Muslim law). In July 2007 he launched a forum for moderate Islam named after himself and funded by the Sharia department of the University of Qatar and the moderate Islamic Center in Kuwait.
Although al-Qaradawi began as a Muslim Brotherhood activist he later denied membership in it and several times even refused to head the movement in Egypt (i.e., to accept the title of general guide). However, he has a special status among members of the Muslim Brotherhood and Hamas, its Palestinian branch, and the Islamic movement in Israel, for all of whom he is the supreme authority on Islamic law.
Ideology, political activity, and publications
Al-Qaradawi refers to his religious views as “moderate Islam,” which seeks to balance intellect and emotion. He has positive attitudes toward reforms in Islam, which he calls “correcting perceptions which were corrupted.” He is considered one of the foremost propounders of the doctrine of “the law of the Muslim minorities” (fiqh al-aqalliyyat), which provides the Muslim minorities around the globe with space in which to maneuver and compromise between their daily lives and Islamic law. The aim of implementing his doctrine is to unite and unify Muslim minorities to make it possible for them to live under non-Muslim regimes, until the final stage of spreading Islam to the entire world.
At the same time, building a bridge between the exigencies of Muslim emigrants’ daily lives and Islamic religious law also includes regarding Europe as Islam’s next target. In 2003 Al-Qaradawi issued a fatwa declaring that “Islam will return to Europe as a victorious conqueror after having been expelled twice. This time it will not be conquest by the sword, but by preaching and spreading [Islamic] ideology […] The future belongs to Islam […] The spread of Islam until it conquers the entire world and includes the both East and West marks the beginning of the return of the Islamic Caliphate […]”
Conservative Muslims object to what they consider Al-Qaradawi’s excessive flexibility and have occasionally attacked his fatwas as “too permissive.” However, despite the criticism he is greatly respected and esteemed in the Muslim world and most Muslim clerics respect his fatwas. Many people today consider him the heir of Sayyid Qutb (Muslim Brotherhood radical theoretician and senior activist in Egypt) and as the movement’s highest religious and ideological authority, even if he did reject offers to officially head it.
Al-Qaradawi has issued a great many fatwas and written a large number of books, the most important of which is The Lawful and Prohibited in Islam. It was translated into many languages and has sold millions of copies. Today it is considered the best selling Muslim book in Europe after the Quran.
Al-Qaradawi’s attitude towards suicide bombing attacks and support for Hamas
All of Al-Qaradawi’s opinions regarding Israel are extreme and he is a source of supreme religious authority for Hamas. He is an enthusiastic supporter of Palestinian terrorism, including when it is directed against civilians, claiming that it is a legitimate expression of the so-called “resistance” and that Israel is a militaristic society where every civilian is a potential soldier.
He issued fatwas calling for jihad against Israel and the Jews and authorizing suicide bombing attacks, even when they entailed killing women and children. He also issued a fatwa authorizing attacks on Jews around the world because in his view there is no essential difference between Judaism and Zionism, and therefore every Jewish target equals an Israeli target.
His status as a leading Sunni-Muslim cleric lends added importance to his fatwas supporting Palestinian terrorism and makes him particularly influential in shaping anti-Israeli sentiments in the Muslim and Arab world.
In July 2003, during the height of the suicide bombing terrorism (during the second intifada), he addressed the issue of suicide bombing attack at an ECFR conference. He said that istishhad (death as a martyr for the sake of Allah),[76] carried out by the Palestinian organizations to oppose the so-called “Zionist occupation”, was by no means to be defined as terrorism (Al-Sharq al-Awsat, July 19, 2003). On other occasions he also supported suicide bombing attacks, including on the BBC (February 8, 2010) and Al-Jazeera TV (January 28, 2009).[77]
Senior Hamas figures relied on Al-Qaradawi’s fatwas which authorize suicide bombing attacks against Israel to justify that sort of (controversial) attack. For example:
a. Sheikh Hamed al-Bitawi, senior Hamas activist in Judea and Samaria, relying on an Al-Qaradawi fatwa, said that according to Islamic jurisprudence, “jihad is a collective duty (fard kifaya) […]” and that if infidels occupy any bit of Muslim land — such as the occupation of Palestine by the Jews, jihad becomes the duty of every individual (fard ‘ayn), thus making it permissible to carry out suicide bombing attacks.[78]
b. Dr. Abd al-Aziz al-Rantisi, a senior Hamas leader who died in a targeted killing, relying on a fatwa issued by Al-Qaradawi, said that “suicide depends on intention. If the person intends to kill himself because he is fed up with life, that is suicide (which is prohibited). However, if he wants to die to strike at the enemy and to receive a reward from Allah, he is considered as delivering up his soul [and not as committing suicide].”[79]
To help fund Hamas’ civilian infrastructure (the da’wah) Al-Qaradawi established the Union of Good, which he heads today. It is an umbrella network which raises money for Hamas and other Islamist activities around the globe. The Union of Good was declared a terrorism-sponsoring organization and outlawed by Israel in February 2002. In December 2002 it was designated as a terrorist organization by the United States and outlawed.
Al-Qaradawi is hostile to the Palestinian Authority. At the beginning of 2010 he criticized Mahmoud Abbas for his vote regarding the Goldstone Report, and issued a fatwa calling for Mahmoud Abbas to be stoned in Mecca. Mahmoud Abbas demanded a retraction from Al-Qaradawi, who denied having issued the fatwa. However, he did admit that during a sermon he said that if accusations against any person in the Palestinian Authority were proved true [i.e., that he had supported the cancellation of the vote on the Goldstone Report], that person should be stoned in Mecca as punishment for treason (IslamOnline, January 7, 2010). In response Mahmoud al-Habash, Palestinian Authority minister of religion and endowments, said that his ministry had ordered all the preachers in the mosques in the Palestinian Authority to attack Al-Qaradawi personally (Al-Quds Al-Arabi, January 18, 2010).
Anti-Semitic statements
Al-Qaradawi has often made anti-Semitic statements. For example, his “Life and Islamic Law” program, broadcast on Al-Jazeera TV on March 15, 2009, discussed the topic of righteous Muslims in Islam. One of the viewers called in and asked about the role of the righteous (al-salihun) in the Quran in the liberation of the (Islamic) holy places and the victory of the (Muslim) nation.
Al-Qaradawi used the opportunity to attack the Jews, basing his answer on a known hadith (oral tradition) calling for the killing of Jews. On the program he said that righteous Muslims were “the salt of the earth” who were always instrumental in liberating lands. He called them a source of hope and said he hoped that through them Jerusalem would be “liberated,” as would “Palestine,” the Gaza Strip, and all the lands ruled by the enemies of the Muslims. He said that the war against the Jews was not only the war of the Palestinians but of all Muslims.
Al-Qaradawi based his answer on a well-known hadith about the war on Judgment Day between Muslims and Jews. He said that the prophet Muhammad said that “…therefore you will continue to fight the Jews and they will fight you until the Muslims kill them. The Jew hides behind rock and tree. The rock and the tree say, oh, slave of Allah, oh, Muslim, here is the Jew behind me, come and kill him.”[80] He interpreted that to mean that those who fight to “liberate” the holy places are the Muslim slaves of Allah, and not Jordanians or Palestinians or Egyptians or Iraqis.
Al-Qaradawi’s position on Al-Qaeda and the global jihad
Al-Qaradawi denounced the September 11, 2001 attacks on the World Trade Center in New York and said it was the duty of every Muslim to help bring the perpetrators to trial. However, as opposed to his opposition to Al-Qaeda, he called for attacks on Americans fighting in Iraq.
In August 2004 a conference titled “Pluralism in Islam” was held by the Egyptian union of journalists in Cairo. At the conference Al-Qaradawi issued a fatwa allowing the abduction and murder of American civilians in Iraq to exert pressure on the American army to remove its forces. He emphasized that “all Americans in Iraq are fighters, there is no difference between civilians and soldiers, and they have to be fought against because the American civilians come to Iraq to serve the occupation. Abducting and killing them is a [religious] duty to make [the Americans] leave [Iraq] immediately. [On the other hand] mutilating their corpses is forbidden by Islam” (Al-Sharq al-Awsat, London, September 2, 2004).
Al-Qaradawi issued the fatwa a week after public figures from various Muslim countries published an open letter calling to support the forces fighting the Western coalition in Iraq. It was signed by 93 Islamic clerics and public figures, including Al-Qaradawi and members of the Muslim Brotherhood, Hamas, the Palestinian Islamic Jihad and Hezbollah (Al-Quds Al-Arabi, London, August 23, 2004).
In view of the storm caused by the fatwa permitting the abduction and murder of American civilians in Iraq, ten days later Al-Qaradawi sent a fax to the London-based Arabic daily Al-Hayat denying “what the media said he had said.” “Some of the media claimed I issued a fatwa saying it was a duty to kill American civilians in Iraq,” Al-Qaradawi said. “That has no basis. I never issued a fatwa about that issue. A few days ago I was asked at the Egyptian union of journalists whether it was permissible to fight against the occupation in Iraq and I answered in the affirmative. After that I was asked about American civilians in Iraq and I answered only with a question: Are there American civilians in Iraq? It is well known that I do not use the word ‘kill’ in a fatwa but rather ‘struggle,’ which is broader and does not necessarily refer to killing. In addition, on several past occasions I denounced abducting hostages and demanded they be released without threatening to kill them” (Al-Hayat, London, September 9, 2004).
Before the denial was issued, Al-Qaradawi’s office manager Issam Halima confirmed that Al-Qaradawi had issued a fatwa stating that it was a duty to fight the American civilians in Iraq because they were invaders (Al-Quds Al-Arabi, London, September 23, 2004).
Al-Qaradawi and Iran
Al-Qaradawi strenuously opposes attempts to disseminate Shi’ite Islam and is critical of Iran’s attempts to spread it to Sunni countries. He has also criticized Hezbollah leader Hassan Nasrallah on a number of occasions.
The call for Muslims to acquire nuclear weapons
In the past Al-Qaradawi said that Muslims should acquire nuclear weapons “to terrify their enemies.” However, he said that nuclear weapons should not be used.[81]
Al-Qaradawi’s position on the uprisings in Tunisia and Libya
Regarding the recent events in Tunisia, Al-Qaradawi said that the struggle should be continued until all members of Ben Ali’s party are removed from their positions, with the exception of the interim president, who should, he said, remain in power to prevent the creation of a constitutional vacuum. He called on Tunisia to release political prisoners, bring back political exiles, and restore the Islamic customs which were forbidden by the ousted president’s secular regime, such as wearing the veil (hijab) on university campuses.
Regarding the recent events in Libya, Al-Qaradawi called on Muammar Gaddafi to relinquish power and learn the lessons of Egypt and Tunisia. He said that a revolt against Gaddafi was an Islamic religious duty, calling on the members of the tribes in Libya to rise up against Gaddafi and join the ranks of the demonstrators. He called on the Libya army “to behave like their brothers in Egypt, to stand alongside the people to restore to Libya its Arab Islamic character.” He asserted that those who had died during the violent events in Libya were martyrs in paradise and supported the jihad fighters rising up against the Libyan regime (Egyptian TV, telephone conversation with Al-Qaradawi broadcast in a special program, February 20, 2011).
This comprehensive analysis of the Muslim Brotherhood (by ITIC) consists of 12 chapters. All 12 chapters are listed below:
Chapter 1: The historical evolution of the Muslim Brotherhood in Egypt
Chapter 2: The ideology of the Muslim Brotherhood
Chapter 3: The Muslim Brotherhood’s education, preaching, and social activity
Chapter 4: The structure and funding sources of the Muslim Brotherhood
Chapter 6: The Muslim Brotherhood’s stance on the Palestinian-Israeli conflict
Chapter 7: The development of political discourse in the Muslim Brotherhood and the 2007 election platform
Chapter 8: Profiles of prominent Muslim Brotherhood figures in Egypt
Chapter 9: The Egyptian Muslim Brotherhood’s ties to its branches in Middle Eastern and Western countries
Chapter 10: The Muslim Brotherhood in other Arab countries and in Europe
Chapter 11: A profile of Sheikh Dr. Yusuf al-Qaradawi
Chapter 12: Islamic jihadist organizations in Egypt ideologically originating in the Muslim Brotherhood
You can download the full study in PDF-format here
Notes:
[76] The suicide bomber is called istishhadi, the one who deliberately sacrifices himself for the sake of Allah.
[77] According to MEMRI, February 8, 2010.
[78] Al-Hayat, February 25, 2001.
[79] Al-Hayat, February 25, 2001.
[80] According to the original hadith, every tree and rock will give up the hiding places of the Jews except the nitraria, (a thorny bush which grows in desert regions). In other versions, such as that quoted by Al-Qaradawi, the words of Muhammad are not related to Judgment Day but used rather in their current political contexts and as a general commandment to Muslims to kill Jews, with no mention of the protection theme.
[81] Qatari TV, October 18, 2002, according to MEMRI.



 RSS
RSS












A profile of Sheikh Dr. Yusuf al-Qaradawi | #Egypt #Islamism http://bit.ly/nHrovK
A profile of Sheikh Dr. Yusuf al-Qaradawi | #Egypt #Islamism http://bit.ly/nHrovK
[…] Chapter 11: A profile of Sheikh Dr. Yusuf al-Qaradawi […]
[…] Muslim Brotherhood’s spiritual leader’s call for jihad extends not only to the conquest of Israel and the killing of Jews. It includes the […]
[…] Muslim Brotherhood?’s spiritual leader’s call for jihad extends not only to the conquest of Israel and the killing of Jews. It includes the […]